Active Transport Carriers Are Best Described as
Primary active transport directly uses the metabolic energy in the form of ATP to transport molecules across the membrane. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradientthat is if the concentration of the substance inside the cell is greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid and vice versathe cell must use.

Active Transport Co Transport 2 4 10 Aqa As Biology Revision Notes 2016 Save My Exams
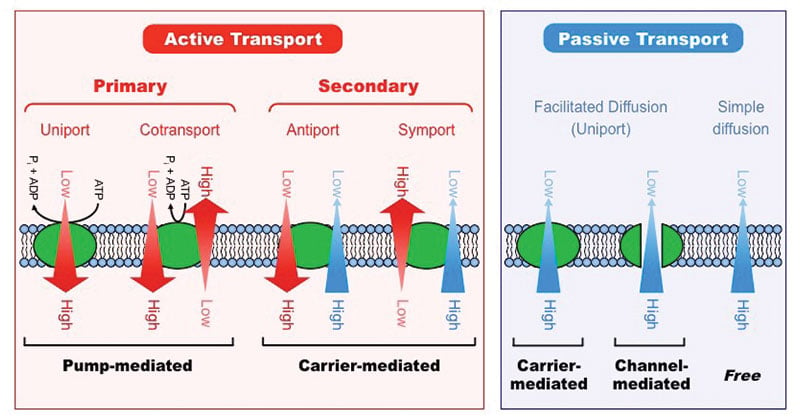
Uniporters symporters and antiporters.

. 27 Which one of the following best describes the electron transport chain. The energy for active transport comes from ATP generated by respiration in mitochondria. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive changes.
Both allow for the flow of molecules into and out of a cell. The transport proteins responsible for secondary active transport are referred to as secondary active transporters and are specifically referred to as cotransporters also known as symporters and exchangers also known as antiporters. Both directly connect the membrane to the nucleus of a cell.
Active transport mechanisms collectively called pumps or carrier proteins work against electrochemical gradients. The primary active transport is of utmost obvious in the sodiumpotassium pump NaK ATPase which regulates the resting potential of the cell. Transmembrane carrier proteins are involved in active transport.
Active transportation is influenced by temperature. Moving against a gradient. Active transport can best be described as.
With the exception of ions small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cells energy usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP. Carrier Proteins for Active Transport.
Many of the carrier proteins involved in active transport are referred to as pumps because analogous to a water pump which requires energy to crank the handle up and down to make water flow transport pumps. Active transport as stated earlier is mediated by carrier proteins that undergo conformational changes in order to move solutes across membranes. In active transport carrier proteins are required.
Why is active transport such an important cell process. Part 15 Active transport can best be described as Multiple Choice the diffusion of water from areas where water concentration is higher to areas where water concentration is lower. D Glucose is broken down to a three-carbon.
Plants transport their nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion. A multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the molecular unit of energy currency in intracellular energy transfer. Main Difference Primary vs Secondary Active Transport.
A uniporter carries one specific ion or molecule. Passive transportation is not influenced by temperature. The energy-free hydrolysis of ATP is used to force three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell.
The moving of molecules from areas of high concentration to that of low concentration to gain energy is best described as. Cotransport and cotransporters are also commonly written as co-transport and co-transporters respectively. We covered these two processes in class today and the teacher is to give you a test on them in the next class.
The diffusion of water from areas where water concentration is higher to areas where water concentration is lower. The movement of molecules with their concentration gradient from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. They are primary active transport and secondary active transport.
Define and describe active transport. Passive transport is a comparatively slow process. Take up the review questions before your next biology class.
Active transport is a rapid process. Both use energy to continuously move water molecules out of a cell. Transpires in one direction.
Carrier proteins such as uniporters symporters and antiporters perform primary active transport and facilitate the movement of solutes across the cells membrane. Active transport can best be described as the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. The sodium-potassium pump requires a carrier protein that binds.
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy. Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein carriers.
These transmembrane proteins are run by ATP. Only active transport can move a substance from an area where it has a lower concentration to an area where it has a higher concentration. Both cause the phospholipid bilayer to form a rigid membrane for a cell.
All the best in. Active Transport Active transport is the energy-demanding transfer of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration gradient ie from lower concentration to higher concentration. There are three types of these proteins or transporters.
Only active transport can move a hydrophilic substance across the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. Active transport mechanisms do just this expending energy often in the form of ATP to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. An important membrane adaption for active transport is the presence of specific carrier proteins or pumps to facilitate movement.
Key Terms adenosine triphosphate. The primary function of molecular membranes is the transport of ions and molecules in and out of cellstransport is directional and selective. Biology questions and answers.
C Electrons are pumped across a membrane by active transport. A Electrons are passed from one carrier to another releasing a little energy at each B Hydrogen atoms are added to CO2 to make an energy-rich compound. The carrier proteins that transport molecules by.
Active transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient with the assistance of enzymes and usage of cellular energy. Active transport is divided into two types known as primary and secondary active transport depending on the source of energy used in. Two types of active transports can be identified in a cell.

Carrier Protein Definition Function And Examples Biology Dictionary
Active Vs Passive Transport Definition 18 Differences Examples

4 10 Facilitated Diffusion Of Solutes Plasma Membrane Facilitated Diffusion Study Biology
Comments
Post a Comment